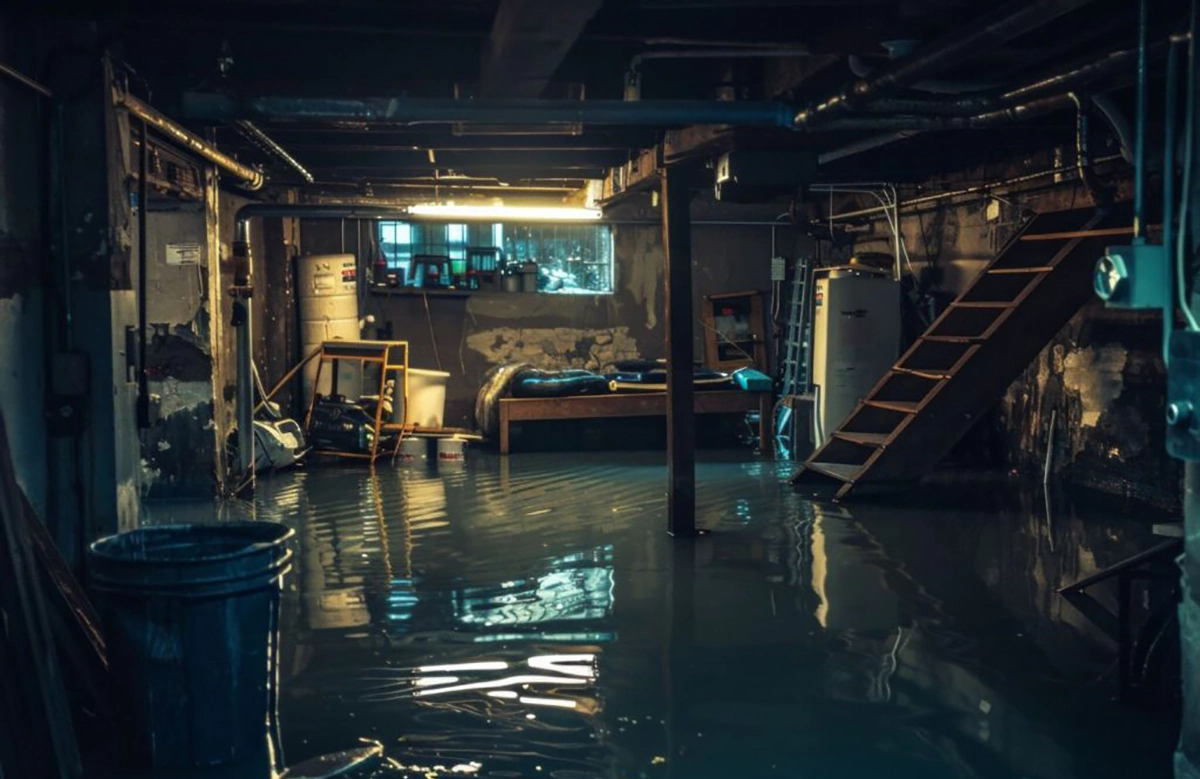
Basement flooding is a homeowner’s nightmare, especially when it’s caused by something as seemingly minor as a poorly designed window well. Window wells serve a crucial function in protecting your basement from water intrusion, but when they are improperly designed or installed, they can become the very source of leaks and flooding. In this article, we’ll explore how poor window well design can lead to basement flooding, uncover the hidden role of window wells in basement protection, and identify common design mistakes that cause flooding. We’ll also share practical solutions including window well waterproofing and drainage fixes — especially relevant for homeowners in Toronto facing this issue.
The Hidden Role of Window Wells in Basement Protection
Window wells are recessed structures installed outside basement windows to keep soil, water, and debris away from the window itself. They create a barrier between the window and the earth, allowing natural light into your basement and providing an emergency exit in some cases.
However, window wells are more than just structural features — they are integral to your home’s waterproofing system. Properly designed and installed window wells:
- Divert rainwater and groundwater away from basement windows.
- Prevent soil erosion around window openings.
- Enable effective drainage to reduce hydrostatic pressure against basement walls.
- Help maintain the integrity of basement window seals.
When window wells perform their function well, they reduce the risk of basement flooding. But when the design is poor, these wells can trap water against the window or basement wall, causing leaks and eventual flooding.
Common Design Mistakes That Cause Flooding
Many homeowners are unaware that window well problems can originate from simple but critical design flaws. Here are some of the most common mistakes that lead to basement flooding:
1. Lack of Proper Drainage
One of the biggest mistakes is failing to include adequate drainage in the window well. Without a drain, water collects inside the well, saturating the soil and exerting pressure against the basement window and wall. Over time, this leads to water seeping through cracks and joints.
2. Incorrect Window Well Size or Shape
Window wells that are too small or shaped improperly may not divert enough water away from the basement window. This can cause water to pool and remain in contact with the window frame, increasing the chance of leaks.
3. Poor Window Well Waterproofing
If the window well and surrounding basement wall are not waterproofed correctly, moisture will easily penetrate through. Neglecting to apply waterproof membranes or sealants around the window well is a common oversight.
4. Improper Grading Around the Window Well
The soil grade around the window well must slope away from the house. If the grading directs water toward the window well, flooding risk skyrockets.
5. Absence of a Window Well Cover
Window well covers protect the well from leaves, debris, and heavy rainfall. Without a cover, debris clogs drainage, and water volume inside the well increases drastically.
CTA:Don’t wait for water to damage your basement! Contact our window well waterproofing experts in Toronto and schedule your free consultation today.
Window Well Waterproofing and Drainage Solutions
The good news is that most basement flooding caused by window wells can be prevented or fixed with the right solutions. Here’s what experts recommend:
Fix Window Well Drainage
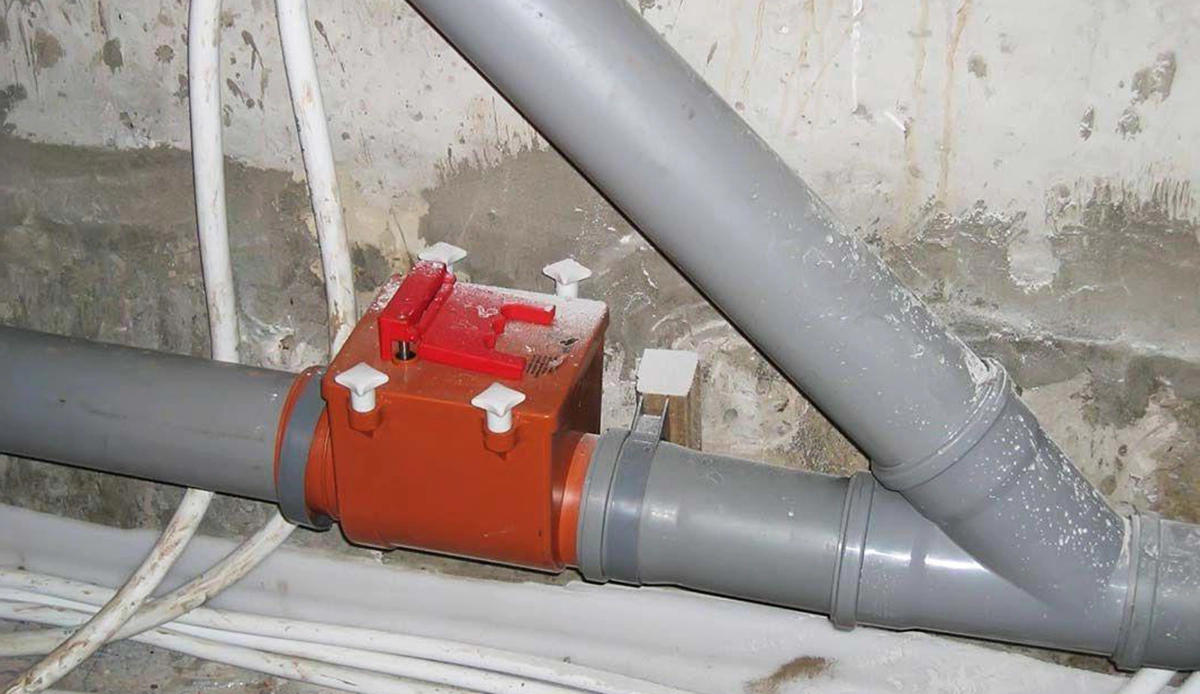
Installing or repairing drainage systems inside window wells is essential. This often includes adding gravel, drain pipes connected to the home’s foundation drainage system, and ensuring water is directed away from the house. Proper drainage prevents water accumulation and reduces pressure on basement walls.
Professional Window Well Waterproofing
Applying waterproof coatings or membranes on basement walls adjacent to window wells seals potential leak points. Modern waterproofing materials offer long-term protection against water intrusion.
Correct Window Well Installation in Toronto
Toronto’s climate includes heavy rains and snow melt, which increases basement flooding risks. That’s why professional window well installation tailored to local conditions is crucial. Proper excavation, drainage, waterproofing, and grading can save you costly repairs down the line.
Window Well Covers
Adding durable, clear window well covers helps keep debris and excess water out, improving drainage performance.
CTA:Struggling with basement flooding from poor window well drainage? Call us now for a professional inspection and effective solutions to fix your window well drainage!
Basement Flooding from Window Wells: Why You Should Act Now
Ignoring early signs of leaking window wells can lead to major basement flooding, mold growth, structural damage, and expensive remediation. If you notice water pooling around your basement windows or signs of moisture inside, it’s time to get a professional inspection.
By addressing window well design flaws early, you protect your home’s foundation, maintain dry and usable basement space, and avoid headaches caused by water damage.
Why Choose Professional Help for Window Well Problems in Toronto?
Toronto homes face unique drainage challenges due to weather and soil conditions. Expert plumbers and waterproofing specialists understand these issues and offer:
- Customized window well waterproofing solutions
- Expert drainage system installation and repairs
- Quality materials designed for Toronto’s climate
- Reliable, long-lasting fixes to keep your basement dry
If you’re experiencing basement flooding from window wells or want to prevent it, contact POM Plumbing’s experienced team today for an assessment and effective solutions tailored to your home.
Final Thoughts
Proper window well design is vital to preventing basement flooding. Don’t overlook the hidden role these structures play in your home’s waterproofing system. With the right drainage, waterproofing, and maintenance, your basement can stay dry even during heavy rains.