Modern plumbing has come a long way from traditional soldering and threading methods. One of the most innovative technologies used today is the ProPress fitting system — a fast, reliable, and clean way to connect pipes without using open flames or messy materials. Whether you’re working with copper, black, or gas pipes, ProPress fittings are changing how professional plumbers in Canada handle installations and repairs.
What Is a ProPress Fitting?
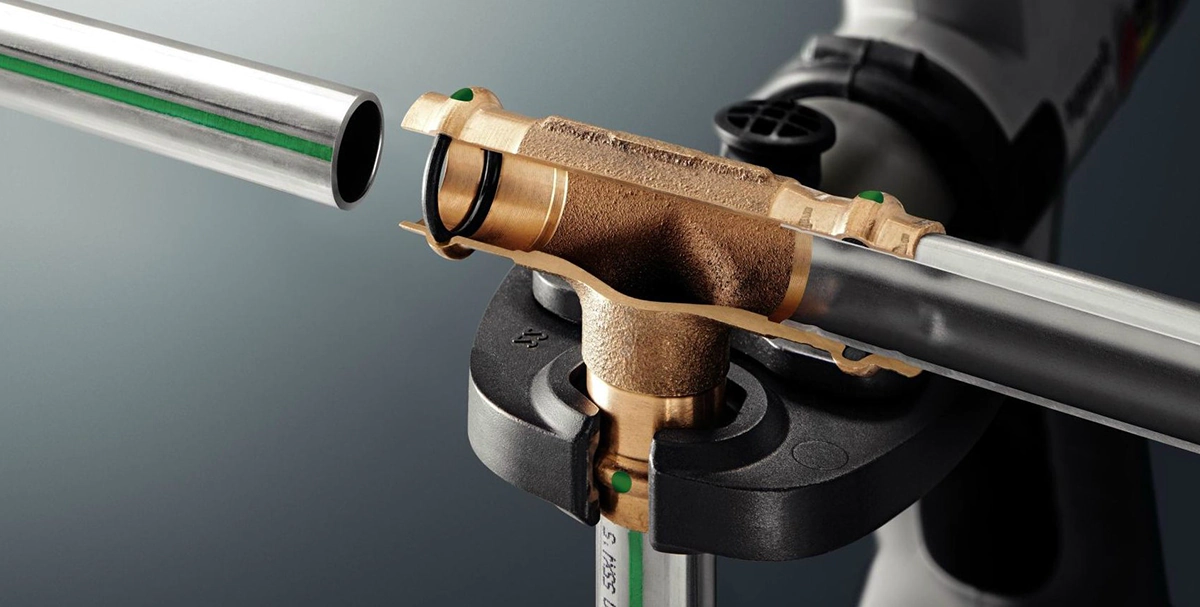
A ProPress fitting is a mechanical connection system designed to join pipes quickly and securely using a pressing tool instead of soldering or welding.
Developed by Viega, the system relies on stainless-steel or copper fittings that feature a built-in sealing element (often EPDM or HNBR). When pressed, the tool permanently deforms the fitting around the pipe, creating a watertight and airtight seal.
Unlike traditional solder joints that require heat, flux, and drying time, ProPress plumbing fittings are installed cold — which means faster and safer work, especially in residential and commercial buildings where open flames could be risky.
How ProPress Fittings Work
The working principle behind ProPress pipe fittings is simple but extremely effective. Each fitting has a specially designed groove and sealing ring. When the pressing tool’s jaws clamp around it, the fitting compresses tightly onto the pipe, locking the seal in place.
This compression ensures:
- A permanent mechanical connection
- No need for drying or cooling time
- Resistance to vibration and mechanical stress
- Excellent performance under pressure
Because no soldering or welding is needed, plumbers can even make connections in wet conditions — a huge advantage during maintenance or emergency repairs.

Main Types of ProPress Fittings
Different piping materials and applications require different types of ProPress systems. Here are the most common ones used in Canada:
1. ProPress Copper Fittings
These are the most widely used and recognized fittings in plumbing systems. ProPress copper pipe fittings are ideal for potable water, heating, and cooling lines.
They offer:
- Corrosion resistance
- Long service life
- Compatibility with standard copper tubing
- Clean, professional look for visible installations
Because they don’t require flame soldering, ProPress copper fittings are safer to install in finished spaces or near combustible materials.
2. ProPress Fittings for Gas Lines
Specially engineered ProPress gas fittings use yellow HNBR seals designed to handle natural gas and propane. These are identified as ProPress G fittings.
They are suitable for:
- Residential and commercial gas lines
- Industrial gas distribution
- Retrofitting or replacing threaded black pipe systems
With ProPress fittings for gas, plumbers can connect lines faster and reduce leak risks associated with traditional threaded joints.
3. ProPress Black Pipe Fittings
For more robust or industrial applications, black pipe ProPress fittings provide high-strength, flame-free connections for steam, compressed air, or oil lines.
ProPress black pipe fittings eliminate the need for threading heavy steel pipe, saving time and reducing tool wear. They also maintain excellent resistance to high pressure and temperature changes.
Advantages of Using ProPress Fittings
The popularity of ProPress plumbing fittings continues to grow because they offer numerous benefits over conventional methods:
1. Speed and Efficiency
A traditional soldered joint may take several minutes to prepare, clean, heat, and cool. With ProPress pipe fittings, connections are completed in seconds — ideal for large installations or tight deadlines.
2. Safety on the Job
Because no flame or flux is required, ProPress fittings eliminate fire hazards. This makes them perfect for hospitals, schools, and commercial sites where open-flame work is restricted.
3. Reliability and Durability
When pressed correctly, ProPress copper fittings create a consistent, long-lasting seal resistant to corrosion, pressure changes, and vibration. Each fitting is tested to meet strict North American plumbing standards.
4. Versatility
From ProPress fittings for gas to ProPress black pipe fittings, the system covers virtually every type of piping — copper, stainless, carbon steel, and more. That’s why professional plumbers across Canada rely on it for everything from water lines to industrial gas systems.
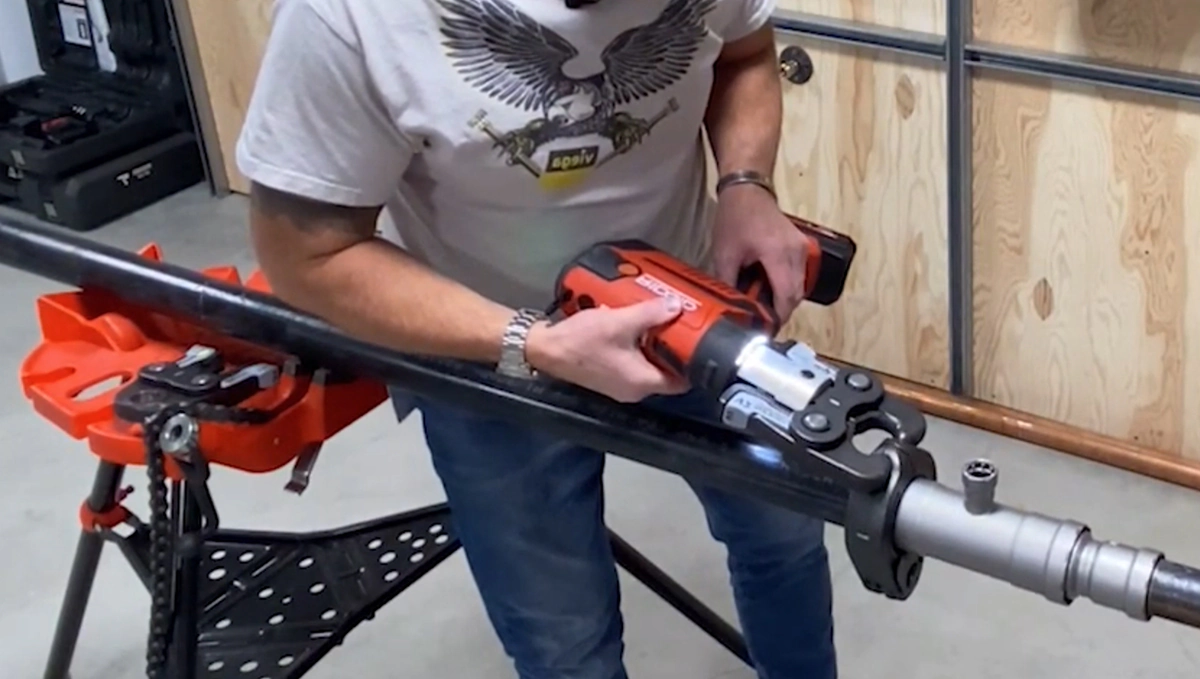

Common Applications in Canada
ProPress fittings in Canada are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing. Some of the most frequent applications include:
- Domestic hot and cold water systems
- Hydronic heating and cooling
- Natural gas and propane installations
- Fire sprinkler and compressed air systems
- Industrial fluid transfer lines
Because the technology minimizes downtime and clean-up, it’s ideal for retrofits in condos, office towers, and public buildings.
How Long Do ProPress Fittings Last?
When properly installed, ProPress copper pipe fittings can last 50 years or more. The combination of strong mechanical connection and corrosion-resistant materials ensures long service life with minimal maintenance.
Regular inspection and pressure testing during installation help guarantee a leak-free system that performs reliably for decades.
Can ProPress Fittings Leak?
Although ProPress fittings are extremely reliable, leaks can occur if:
- The pipe wasn’t cleaned or deburred properly before pressing
- The fitting was not fully inserted
- The press tool wasn’t calibrated or aligned correctly
Professional plumbers, like the experts at POM Plumbing, use certified equipment and follow manufacturer standards to prevent such issues. Each joint is pressure-tested after installation to ensure a perfect seal.
Why Choose ProPress Fittings for Your Plumbing Project
Whether you’re replacing a water line, upgrading gas pipes, or modernizing an old heating system, ProPress plumbing fittings offer speed, safety, and long-term reliability.
They are an investment in quality workmanship — one that pays off through fewer leaks, shorter installation times, and lower maintenance costs.
For homeowners and contractors alike, POM Plumbing provides expert installation of ProPress pipe fittings across Toronto and the GTA. Our licensed plumbers work with copper, gas, and black pipe systems, ensuring every joint is secure, compliant, and built to last.
Final Thoughts
The ProPress fitting system represents the future of plumbing — clean, efficient, and professional. It replaces outdated soldering methods with a safer and faster alternative that maintains exceptional strength and performance.
If you need reliable installation or repair using ProPress fittings in Canada, contact POM Plumbing today. Our specialists will help you choose the right solution for your copper, gas, or black pipe system and guarantee results that stand the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. ProPress fittings are ideal for both new installations and retrofits. Plumbers can easily connect ProPress copper pipe fittings to existing copper lines by cleaning the pipe and pressing on the new fitting — no need to drain the entire system or use a torch. This makes them perfect for repairs in occupied homes or commercial spaces.
ProPress fittings can be used outdoors if properly protected from moisture, UV exposure, and soil contact. However, for underground installations, additional corrosion protection or specific underground-rated fittings should be used. Always follow local Canadian plumbing codes to ensure compliance and longevity.
No. Once a ProPress fitting has been crimped, it cannot be reused. The pressing process permanently deforms the metal around the pipe, and removing it compromises the seal. If you need to modify a line, the old fitting must be cut off and replaced with a new one.
To install ProPress plumbing fittings, plumbers use a hydraulic or battery-powered press tool equipped with the correct jaw size. The tool applies precise pressure to compress the fitting onto the pipe. Using certified tools is crucial for maintaining a watertight and gas-tight connection that meets manufacturer specifications.
Many ProPress pipe fittings come with a “Smart Connect” feature — a small leak path that allows unpressed connections to drip slightly during pressure testing. This alerts plumbers to any missed joints before the system goes live. Once pressed, the leak stops instantly, confirming a secure connection.
Yes. ProPress fittings for gas (known as ProPress G) are specifically designed for natural gas and propane systems. They use yellow HNBR seals that resist gas and high temperatures. These fittings are approved for use across Canada under local gas codes, provided installation follows manufacturer instructions.
Depending on pipe size and material, ProPress copper fittings can handle up to 200–300 PSI for water systems and up to 150 PSI for gas. This makes them suitable for residential plumbing, hydronic heating, and many commercial applications. Always verify pressure ratings based on the specific product type and system design.
ProPress plumbing fittings offer faster installation, no flames, and fewer leak risks compared to soldering or threading. While soldering requires heating and cooling time, pressing takes only seconds. Threading heavy steel pipe also demands more labor and tools. ProPress simplifies all of that while maintaining durability and code compliance.
Once installed correctly, ProPress pipe fittings need minimal maintenance. Routine inspection for external corrosion, especially in humid or chemical environments, is recommended. Systems should also be pressure-tested annually in commercial or industrial applications to ensure long-term reliability.